intelligentCHILD
Building an AI-powered health assistant for young mothers
Overview
My research team at the Texas A&M Health Science Center wanted to address the problem of how disadvantaged mothers in underserved areas of Texas typically experience low health literacy and limited medical resources. To make their obstacle worse, conventional search engines, like Google, have little consideration of user location and needs, making it difficult to find local and accessible healthcare services.
intelligentCHILD (iCHILD) is a semantic search engine designed to empower vulnerable populations by providing access to contextually accurate, vetted resources through a conversational, natural-language interface
I was hired as a front-end developer to help transform the existing iCHILD project into a publicly accessible platform. The iCHILD project was originally created by a group of senior computer science students as part of their capstone, but it needed significant redevelopment to reach production-level quality. My work involved redesigning and rebuilding the entire frontend, as well as collaborating on database architecture and API development to modernize the platform and make it more scalable and user-friendly.
Development
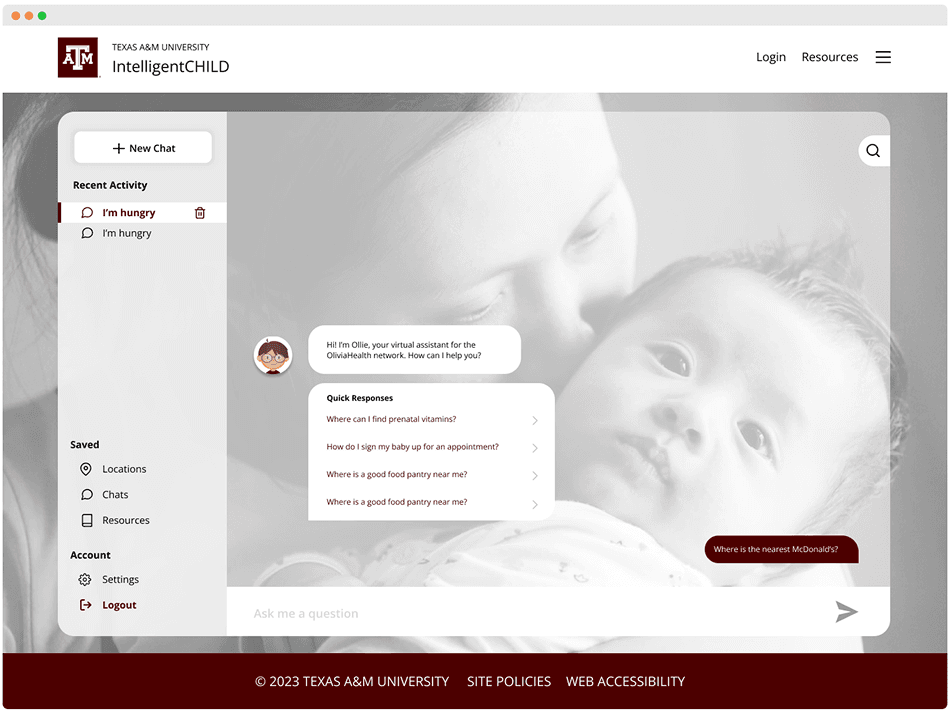
Initially, I focused on rebuilding the frontend of the iCHILD application. The previous version had been developed using a mix of vanilla JavaScript and templating languages, which made it difficult to maintain and extend. I decided to modernize the stack by introducing React.js, TypeScript, and Vite, a combination that significantly improved the app's performance, scalability, and developer experience. This new setup also made the codebase easier to understand and opened the door for future contributors to build on top of it more efficiently.

Working with a designer, we quickly modernized the frontend of the application, creating a sleek, responsive, and user-friendly interface. The new design focused on clean visuals, intuitive navigation, and accessibility, ensuring that users could easily search for resources and interact with the platform across all devices.
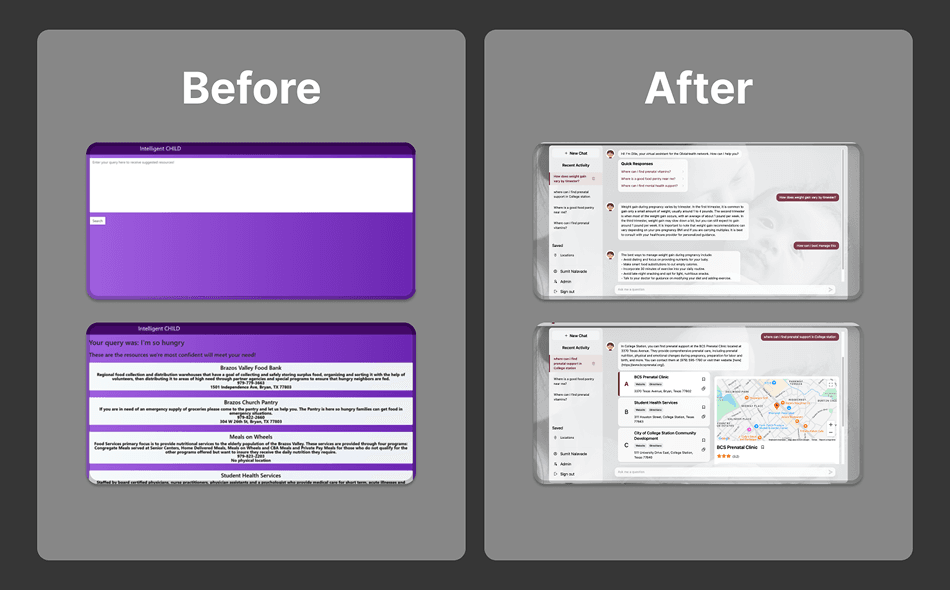
Next, it was necessary to develop the backend APIs from the ground up. My focus was on reliability and simplicity using proven technologies and avoiding unnecessary architectural complexity. The goal was to build a solid, maintainable foundation that could scale as the platform grew, while keeping the system easy to debug and extend for future developers.
Our new backend was built as a monolithic Flask application, serving a collection of RESTful routes for core functionality such as authentication, data retrieval, and resource management. I chose this framework because it struck the right balance between simplicity and flexibility. Flask allowed us to rapidly prototype new features while still providing the structure needed for production-grade reliability. Its lightweight nature made it easy to integrate with our frontend and database, and the large ecosystem of extensions ensured we could easily add functionality like authentication, caching, and API documentation as the platform evolved.

Once the backend was fully developed and integrated with the frontend, it was time to deploy the new application for users. I chose to host the entire platform on an AWS EC2 virtual machine, as it provided full control over the deployment environment, flexible scaling options, and easy integration with other AWS services. This setup allowed us to manage both the frontend and backend within a single environment, simplifying deployment and maintenance while ensuring the system remained stable and responsive under real-world usage.

This marked the completion of our full redevelopment of the iCHILD project, transforming it from the original version built by the computer science students into a modern, production-ready platform. The new application not only looked and felt more polished but was also built with clean, maintainable code and strong engineering practices under the hood. During user acceptance testing (UAT), we saw a significant improvement in user sentiment and feedback.
This milestone opened the door for continued improvements to the project, including enhancing the AI-generated responses and making it easier for our team at the Texas A&M Health Science Center to administer and manage the application. With the foundation rebuilt and modernized, we now have the flexibility to continue evolving the platform adding new features, refining performance, and exploring new ways to integrate AI into healthcare and community resource access.
Challenges - Admin Dashboard
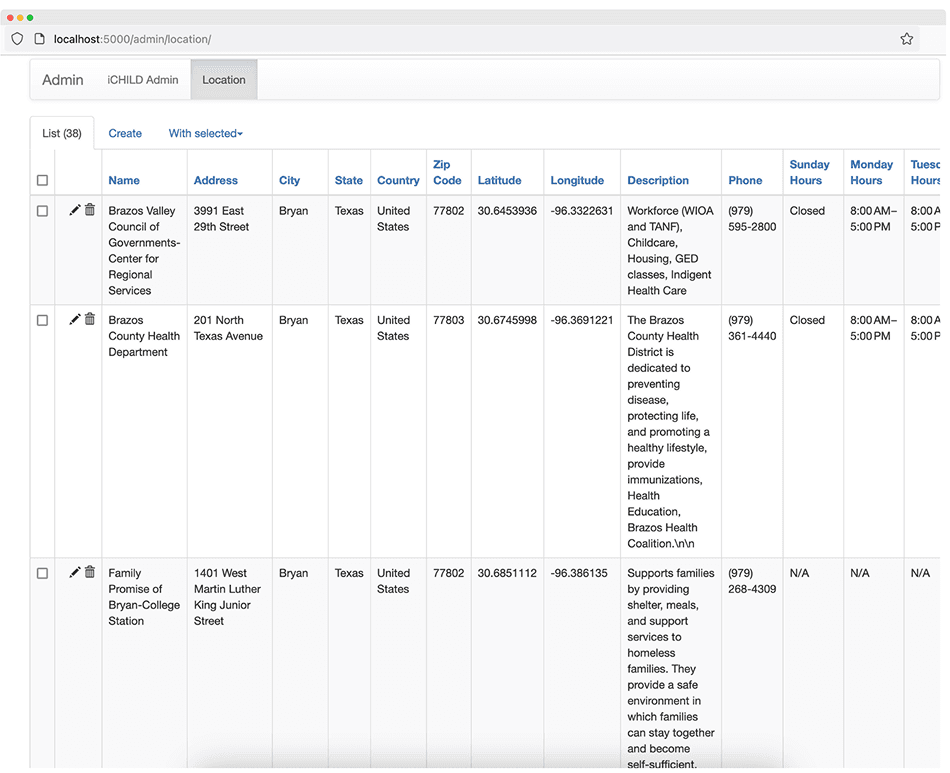
One of the biggest challenges we faced with the iCHILD application was data management. The platform stores a vetted knowledge base of trusted providers including clinics, doctors, nurses, food pantries, and other community resources, all hosted in a database within our AWS VM. While this setup gave us complete control over the data, we encountered challenges in both sourcing new, reliable information and maintaining existing records to ensure accuracy and freshness.
When staff members at the Texas A&M Health Science Center wanted to update the iCHILD database — for example, to add a new provider to recommend to users, they had to contact me directly to make the change manually on the AWS virtual machine. While this process worked, it was inefficient and introduced unnecessary friction. Staffers had no way to view, edit, or manage data themselves, which slowed down updates and made it difficult to keep the provider database fully up to date.
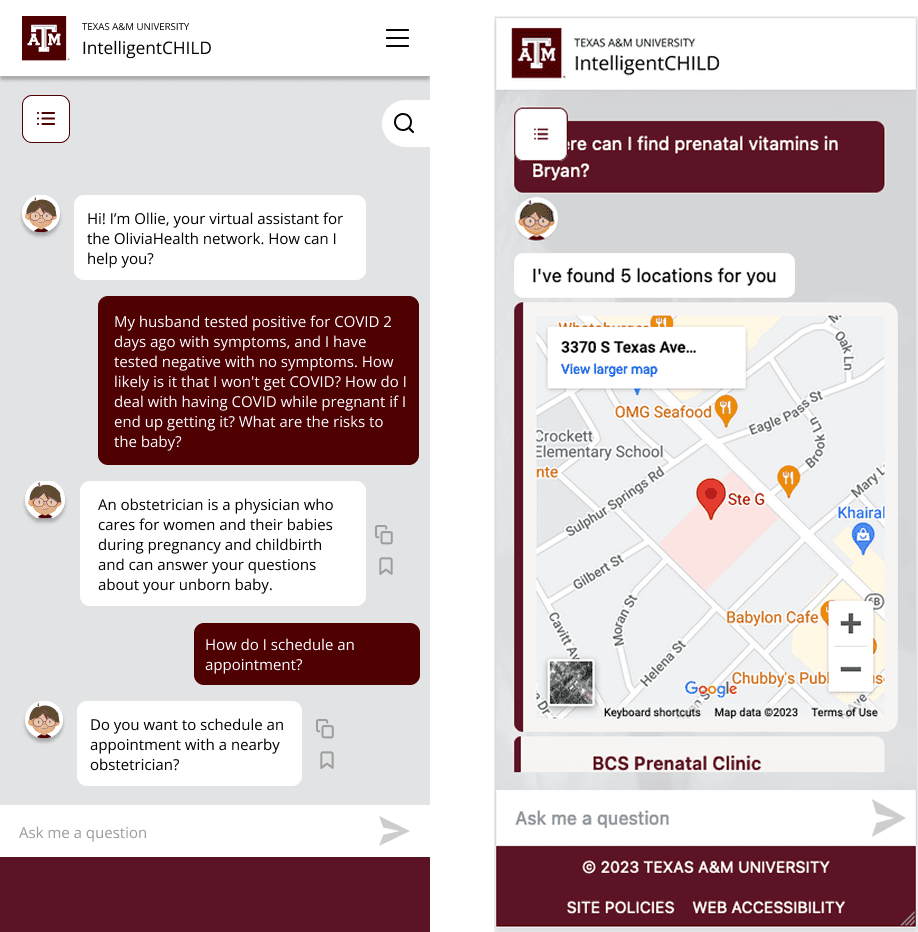
To solve this problem, I led the development of an internal admin dashboard for staff members on our team. Authorized users could log into the iCHILD application using their credentials to gain access to a secure, web-based dashboard. From there, they could view, add, update, and delete data from the knowledge base — including provider listings, contact information, and other relevant details used to generate recommendations and AI responses.
Challenges - Chat Responses
Another major challenge our team faced involved the quality and contextual relevance of the AI-generated responses. While the system could retrieve and generate information from the knowledge base, the responses often lacked precision or context, sometimes pulling in irrelevant details or failing to surface the most appropriate data. We noticed that certain queries didn't consistently retrieve the correct entries from the knowledge base, resulting in answers that were either incomplete or off-topic.
When the previous computer science students developed the system, they used a combination of BERT and a basic keyword-based retrieval method to generate responses. While BERT provided some level of semantic understanding, the retrieval process lacked contextual awareness — it didn't always surface the most relevant information from the knowledge base. As a result, responses were often technically correct but contextually misaligned, especially when multiple similar entries existed.
To improve this, we decided to rebuild the entire response generation process from the ground up. Rather than relying on BERT and keyword-based retrieval, we adopted a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) approach.
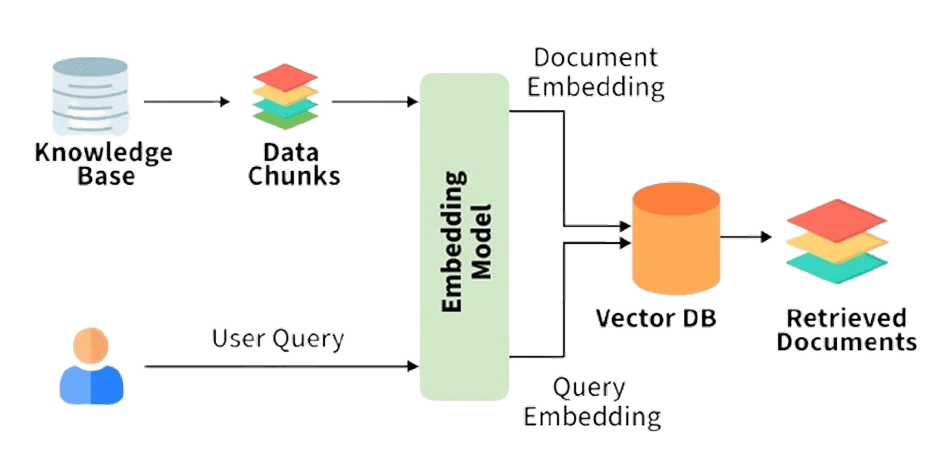
With RAG, each user query is first converted into a vector embedding and compared against the stored embeddings of provider information in the database. The system then retrieves the most semantically relevant entries and feeds them into a large language model, which generates a contextually aware and factually aligned response. This shift dramatically improved the accuracy, consistency, and contextual depth of the system's outputs.
Additionally, we wanted the iCHILD knowledge base to go beyond just physical, brick-and-mortar providers such as clinics, food pantries, and hospitals. The Texas A&M Health Science Center had developed a rich collection of digital resources — including academic journals, articles, infographics, and educational videos — that contained valuable, trustworthy information.
Our goal was to integrate these materials directly into the knowledge base, allowing the AI system to draw not only from location-based data but also from informational and educational content when generating responses. This would enable iCHILD to provide more holistic and informative answers, combining practical service recommendations with evidence-based health knowledge.
We started by aggregating all available data — including information about physical providers as well as the digital assets developed by the Health Science Center. This content was then processed into smaller, meaningful chunks and transformed into vector embeddings, which we stored in the iCHILD database. These embeddings represented the semantic meaning of each piece of information, allowing the system to perform contextual similarity searches rather than relying on exact keyword matches.
When a user submitted a query, the system would convert the query into an embedding and retrieve the most relevant chunks from the database. These retrieved pieces of information were then passed to the LLM, which used them as context to generate an accurate, grounded, and contextually relevant response.
Furthermore, we integrated the new RAG pipeline with the admin dashboard developed earlier. This integration ensured that whenever staff members at the Health Science Center updated the iCHILD knowledge base whether by adding new providers, uploading resources, or editing existing entries, the system would automatically generate new embeddings for the updated content. These embeddings were then stored in the iCHILD database, allowing the platform to instantly reflect the latest information in its responses. As a result, updates made by administrators directly influenced the quality and accuracy of AI-generated answers, keeping the system both dynamic and continuously improving.
Reception + Awards
We released iCHILD to the general public, and the response was overwhelmingly positive. Users appreciated the convenience and reliability of being able to find trusted, vetted information directly through the platform. Many highlighted how helpful it was to have both local provider recommendations and educational health resources available in one place, making it easier to access the care and knowledge they needed.

In addition, we were able to present our work on iCHILD at several conferences including at The Office of Interprofessional Practice, Education, & Research (IPER) at Texas A&M Health Science Center where we won the people's choice award
Personally, I've learned a tremendous amount from working on this project. From full-stack development to AI engineering, iCHILD gave me the opportunity to wear many different hats and gain hands-on experience across the entire product lifecycle. The lessons I learned about building scalable systems, managing data pipelines, and designing for real-world users have carried over into my professional work and continue to shape how I approach engineering challenges and product design today.